A Masked Input field is a special input that visually obfuscates characters to protect sensitive information by masking them with a circular shape.
Usage
When to use
To give users a way to show and hide sensitive information.
When a form input with the ability to mask its value temporarily is needed.
When not to use
For passwords, use the Password input instead.
Masked input vs Password input
The Masked Input is a text field designed to protect sensitive or confidential information while allowing users to show or hide the input value as needed.
The password input is a specific type of form control designed for the secure entry of passwords. The value is always masked or hidden to prevent others from reading the entered characters easily. Unlike the Masked Input, the password input has specific attributes to enhance the security and confidentiality of passwords.
Usage examples
Use the Masked Input to protect sensitive values like secret keys or tokens.
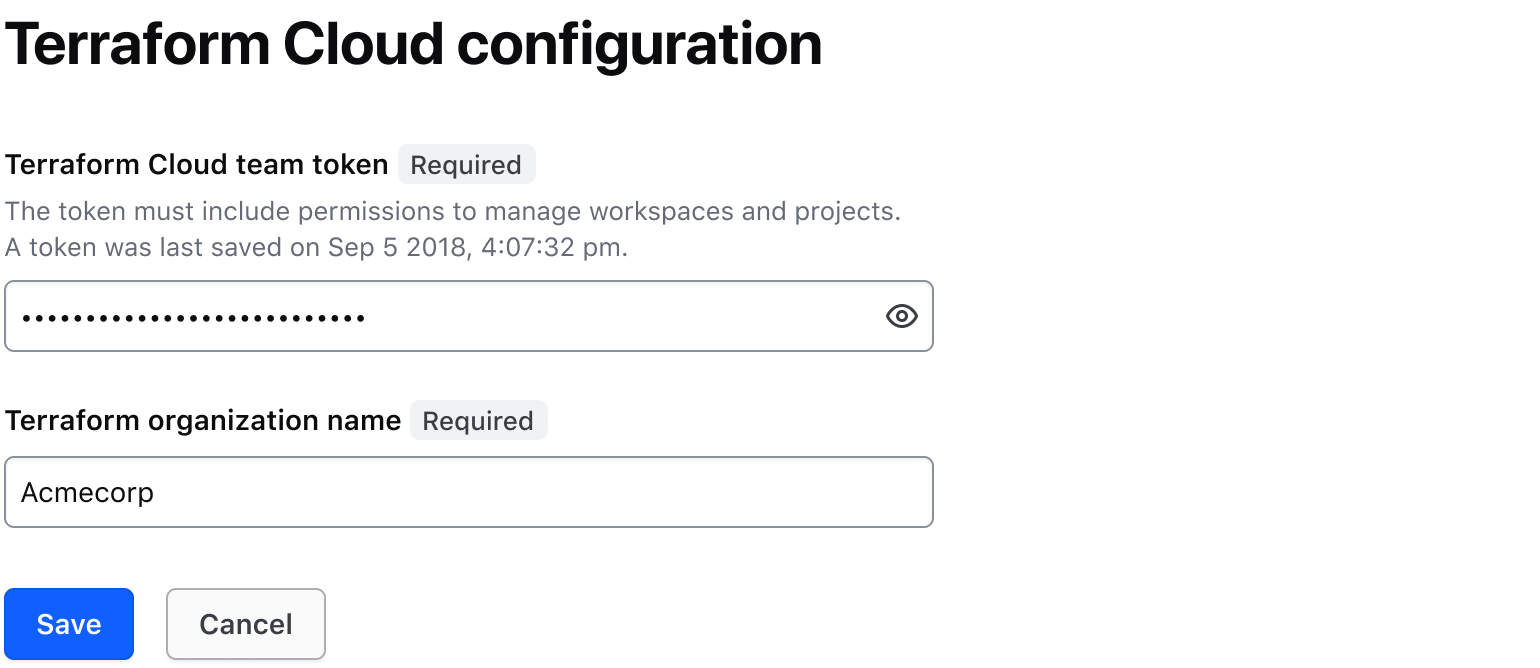
Use the Masked Input to protect sensitive values like variables and certificates from unintended exposure.

Don’t use a Masked Input for password input. Use the Password input.
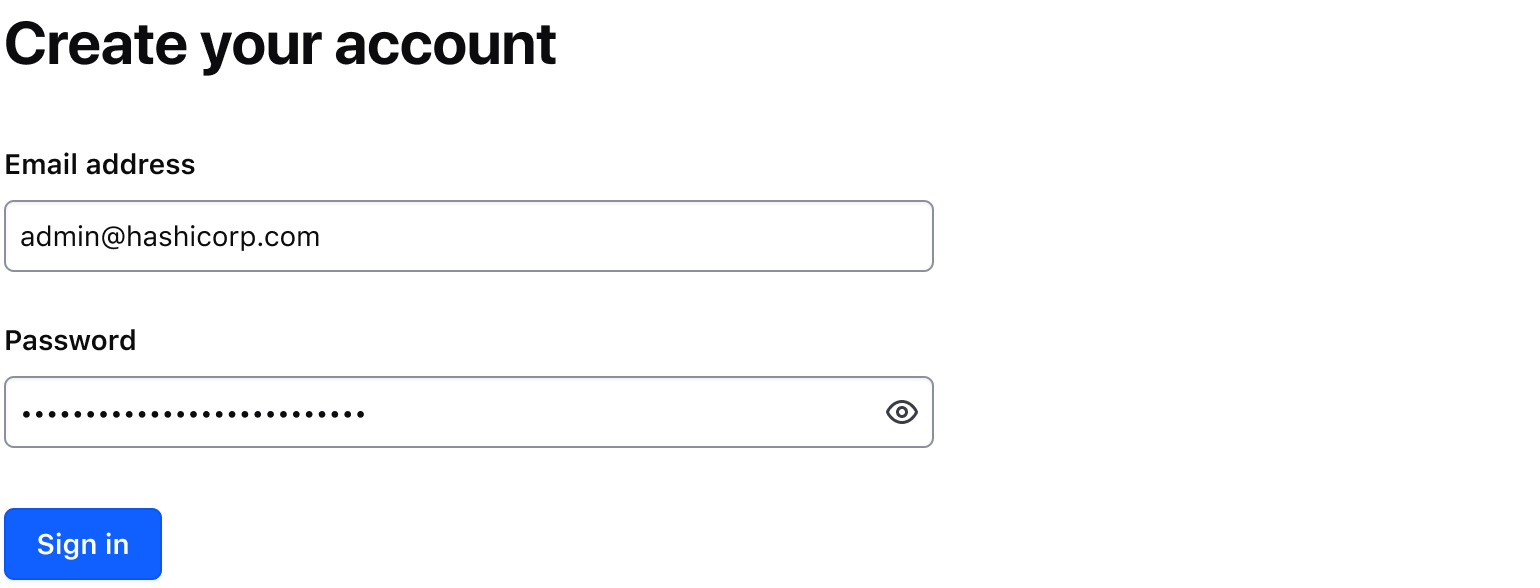
Multiline
Use isMultiline to display multiline textual content. e.g., a Terraform variable. This property replaces the TextInput with a Textarea field.
Required and optional
For complex forms, indicate required fields. This is the most explicit and transparent method and ensures users don’t have to make assumptions. Read more about best practices for marking required fields in forms.
For shorter, simpler forms, indicate optional fields instead.
Copying the Masked Input value
Setting the hasCopyButton property to true will display a Copy Button adjacent to the Masked Input, allowing users to copy the value in the Masked Input to their clipboard. Refer to the Copy Button usage guidelines for more details around copying content.
Character count
For tracking the number of characters entered into a MaskedInput and defining requirements around minimum and maximum length, refer to the Character count documentation.
Error validation
For error validation recommendations, refer to the Form patterns documentation.
Content
For high-level content recommendations, refer to our Primitives documentation.
How to use this component
There are two ways to use the Masked Input component:
Form::MaskedInput::Base- the base component: the input control with a toggle button.Form::MaskedInput::Field- the field component: the input control with a toggle button, a label, helper text, and error messaging (in a wrapping container).
We recommend using the Field component as it provides built-in accessibility functionality. Use the Base component to achieve custom layouts or for special use cases not covered by the Field component.
Form::MaskedInput::Field
The basic invocation requires a Label. This creates:
- a
<label>element with aforattribute automatically associated with the inputIDattribute. - a
<input type="text">or a<textarea>control with an automatically generatedIDattribute.
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field name="demo-team-token" as |F|>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token</F.Label>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
Input value
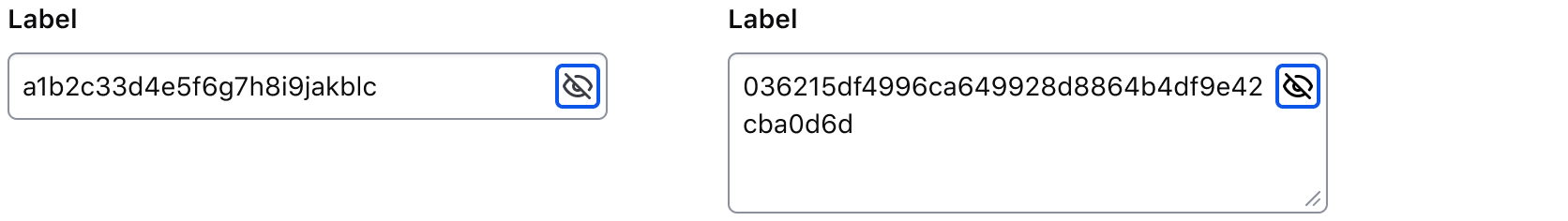
Pass a @value argument to pre-populate the input. By default, the content is visually obfuscated ("masked") and users can make it visible using the associated toggle button.
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field
@value="036215df4996ca649928d8864b4df9e42cba0d6d"
name="demo-team-token"
as |F|
>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token</F.Label>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
If you need to make the content visible by default or control the masking from outside the component, use the @isContentMasked argument.
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field
@isContentMasked={{false}}
@value="036215df4996ca649928d8864b4df9e42cba0d6d"
name="demo-team-token"
as |F|
>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token</F.Label>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
Multiline
Set @isMultiline argument to true to render a <textarea>
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field
@isMultiline={{true}}
@value="-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
MIIBOgIBAAJBAKj34GkxFhD90vcNLYLInFEX6Ppy1tPf9Cnzj4p4WGeKLs1Pt8Qu
KUpRKfFLfRYC9AIKjbJTWit+CqvjWYzvQwECAwEAAQJAIJLixBy2qpFoS4DSmoEm
o3qGy0t6z09AIJtH+5OeRV1be+N4cDYJKffGzDa88vQENZiRm0GRq6a+HPGQMd2k
TQIhAKMSvzIBnni7ot/OSie2TmJLY4SwTQAevXysE2RbFDYdAiEBCUEaRQnMnbp7
9mxDXDf6AU0cN/RPBjb9qSHDcWZHGzUCIG2Es59z8ugGrDY+pxLQnwfotadxd+Uy
v/Ow5T0q5gIJAiEAyS4RaI9YG8EWx/2w0T67ZUVAw8eOMB6BIUg0Xcu+3okCIBOs
/5OiPgoTdSy7bcF9IGpSE8ZgGKzgYQVZeN97YE00
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----"
name="demo-private-key"
as |F|
>
<F.Label>Private key</F.Label>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
Copy button
To allow users to copy the input value to their clipboard, set the @hasCopyButton argument to true.
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field
@hasCopyButton={{true}}
@value="036215df4996ca649928d8864b4df9e42cba0d6d"
name="demo-team-token"
as |F|
>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token</F.Label>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
Helper text
You can add extra information to the field using helper text. When helper text is added, the component automatically adds an aria-describedby attribute to the input control, associating it with the automatically generated ID of the helper text element.
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field
@value="036215df4996ca649928d8864b4df9e42cba0d6d"
name="demo-team-token"
as |F|
>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token</F.Label>
<F.HelperText>The token must include permissions to manage workspaces and projects.</F.HelperText>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
Extra content in label and helper text
The Label and HelperText contextual components used in the Field component yield their content. This means you can also pass structured content.
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field name="demo-team-token" as |F|>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token <Hds::Badge @size="small" @text="Beta" /></F.Label>
<F.HelperText>The token must include <Hds::Link::Inline @href="#">permissions to manage workspaces and projects</Hds::Link::Inline>.</F.HelperText>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
Required vs. optional
Use the @isRequired and @isOptional arguments to add a visual indication that the field is "required" or "optional".
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field @isRequired={{true}} name="demo-team-token" as |F|>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token</F.Label>
<F.HelperText>The token must include permissions to manage workspaces and projects.</F.HelperText>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
<br />
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field @isOptional={{true}} name="demo-team-token" as |F|>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token</F.Label>
<F.HelperText>The token must include permissions to manage workspaces and projects.</F.HelperText>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
Character count
If the user input needs to be limited to a certain number of characters, use @maxLength on a CharacterCount contextual component to guide the user in meeting the length requirements. This property does not restrict the users from entering characters over the limit. To define the maximum string length that the user can enter, set maxlength attribute on the associated input field.
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field
@value={{this.value1}}
name="demo-team-token"
{{on "input" (fn this.updateValue "value1")}}
as |F|
>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token</F.Label>
<F.CharacterCount @maxLength={{40}}/>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
If the user input is required to have a certain number of characters, use @minLength on a CharacterCount contextual component to guide the user in meeting the length requirements.
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field
@value={{this.value2}}
name="demo-team-token"
{{on "input" (fn this.updateValue "value2")}}
as |F|
>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token</F.Label>
<F.CharacterCount @minLength={{30}}/>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
When the user input needs to be in a certain range, use both @minLength and @maxLength on a CharacterCount contextual component to guide the user in meeting the length requirements.
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field
@value={{this.value3}}
name="demo-team-token"
{{on "input" (fn this.updateValue "value3")}}
as |F|
>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token</F.Label>
<F.CharacterCount @minLength={{30}} @maxLength={{40}}/>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
Custom message
For custom messages, you can use the following arguments to build a relevant message: currentLength (the current number of characters in the associated form control), maxLength (the maximum number of characters allowed in the associated form control), minLength (the minimum number of characters required in the associated form control), remaining (the difference between maxLength and currentLength), and shortfall (the difference between currentLength and minLength).
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field
@value={{this.value4}}
name="demo-team-token"
{{on "input" (fn this.updateValue "value4")}}
as |F|
>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token</F.Label>
<F.CharacterCount @maxLength={{40}} as |CC|>
{{CC.remaining}} characters remaining
</F.CharacterCount>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
Validation based on length
You can raise an error based on the number of characters entered into a field using a custom validation function.
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field
@value={{this.value5}}
@isInvalid={{this.fieldIsInvalid}}
name="demo-team-token"
{{on "input" (fn this.updateValue "value5")}}
as |F|
>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token</F.Label>
<F.CharacterCount @minLength={{this.minLength}}/>
{{#if this.fieldIsInvalid}}
<F.Error>Length should be at least 40 characters</F.Error>
{{/if}}
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
Validation
To indicate a field is invalid, use the @isInvalid argument and provide an error message using the Error contextual component.
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field
@isInvalid={{true}}
name="demo-team-token"
@value="036215df4996ca649928d8864b4df9e42cba0d6d"
as |F|
>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token</F.Label>
<F.Error>The provided token is not valid</F.Error>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
Add more than one error message using the more specific Message contextual component.
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field
@isInvalid={{true}}
name="demo-team-token"
@value="036215df4996c649928d8864b4"
as |F|
>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token</F.Label>
<F.Error as |E|>
<E.Message>Length should be at least 40 characters</E.Message>
<E.Message>Should not contain special characters or spaces</E.Message>
</F.Error>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
Custom control ID
If needing a custom ID for the control instead of the one automatically generated by the component, pass the @id argument to the field.
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field @id="tfc-token" name="demo-team-token" as |F|>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token</F.Label>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
Additional aria-describedby
Pass an @extraAriaDescribedBy argument to the field to connect one or more extra elements describing the field to the control. This provides extra ID values to the aria-describedby attribute of the control, in addition to those automatically generated by the component.
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field @extraAriaDescribedBy="my-extra-element-ID" name="demo-team-token" as |F|>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token</F.Label>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
HTML native attributes
This component supports use of ...attributes. This means you can use all the standard HTML attributes of the input control element. This can be useful in case you want to add specific native behaviors to the field, that are not exposed directly by the component (e.g., providing a name for the control, or adding min, max, minlength, maxlength, or pattern attributes to it).
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field name="demo-tfc-token" minlength="40" maxlength="40" name="demo-team-token" as |F|>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token</F.Label>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
Events handling
This component supports the use of ...attributes, which allows you to use all the usual Ember techniques for event handling (e.g., input, blur, change), validation, etc.
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field name="demo-team-token" {{on "blur" this.yourOnBlurFunction}} as |F|>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token</F.Label>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
Custom width
By default, the input control width is set to fill the parent container.
Pass a custom width for the control using the @width argument.
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field @width="250px" name="demo-team-token" as |F|>
<F.Label>Terraform Cloud team token</F.Label>
</Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Field>
Form::MaskedInput::Base
The Base component is intended for rare cases where the Field component can’t be used and a custom implementation is needed. Most of the details for the Field component also apply to the Base component, but see the Component API for more details.
The default invocation creates a <input type="text"> or a <textarea> control with an automatically generated ID attribute.
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Base
@value="036215df4996ca649928d8864b4df9e42cba0d6d"
aria-label="Terraform Cloud team token"
name="demo-team-token"
/>
When the @isMultiline argument is set to true, it creates a <textarea> control with an automatically generated ID attribute. You can also adjust the height of <textarea> either by using the rows attribute or by setting a custom @height value.
<Hds::Form::MaskedInput::Base
@value="-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
MIIBOgIBAAJBAKj34GkxFhD90vcNLYLInFEX6Ppy1tPf9Cnzj4p4WGeKLs1Pt8Qu
KUpRKfFLfRYC9AIKjbJTWit+CqvjWYzvQwECAwEAAQJAIJLixBy2qpFoS4DSmoEm
o3qGy0t6z09AIJtH+5OeRV1be+N4cDYJKffGzDa88vQENZiRm0GRq6a+HPGQMd2k
TQIhAKMSvzIBnni7ot/OSie2TmJLY4SwTQAevXysE2RbFDYdAiEBCUEaRQnMnbp7
9mxDXDf6AU0cN/RPBjb9qSHDcWZHGzUCIG2Es59z8ugGrDY+pxLQnwfotadxd+Uy
v/Ow5T0q5gIJAiEAyS4RaI9YG8EWx/2w0T67ZUVAw8eOMB6BIUg0Xcu+3okCIBOs
/5OiPgoTdSy7bcF9IGpSE8ZgGKzgYQVZeN97YE00
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----"
@isMultiline={{true}}
rows="5"
aria-label="Private key"
name="demo-team-token"
/>
Component API
The Masked Input component has two different variants with their own APIs:
Form::MaskedInput::Base- the base component: the input controlForm::MaskedInput::Field- the field parent component: the input control with label, helper text, and error messaging (in a wrapping container)
Form::MaskedInput::Base
value
string|number|date
Notice: if the string provided contains newline characters they will be stripped, unless
@isMultiline is set to true (this renders the input as a <textarea> element, which supports multi-line text).
isContentMasked
boolean
- true (default)
false to make the input content visible by default or bind it to a variable to control the masking from outside the component.
isMultiline
boolean
- false (default)
<input>. If set to true it renders a <textarea>.
isInvalid
boolean
- false (default)
visibilityToggleAriaLabel
string
- Show masked content (default)
aria-label for the visibility toggle button.
visibilityToggleAriaMessageText
string
- Input content is hidden (default)
aria-live message when the visibility toggle button is pressed.
hasCopyButton
boolean
- false (default)
true, it renders a Copy::Button next to the form control allowing the value of the input to be copied to the clipboard.
copyButtonText
string
- Copy masked content (default)
aria-label for the Copy::Button component.
width
string
@width parameter is provided, the control will have a fixed width. When hasCopyButton is true, the width includes the associated copy button.
height
string
@isMultiline is true. By default, the <textarea> has a height determined by the browser to accommodate 4 lines of text. If a custom @height value is provided, the control will have a fixed height.
…attributes
...attributes.
The attributes will be applied to the input control element. This means you can use all the standard HTML input attributes and all the usual Ember techniques for event handling, validation, etc.
Examples of HTML input attributes:
id, name, placeholder, disabled, readonly, required. See the whole list of attributes. Examples of Ember modifiers: {{on "input" [do something]}}, {{on "change" [do something]}}, {{on "blur" [do something]}}.
Form::MaskedInput::Field
id
string
By default, the ID is automatically generated by the component. Use this argument to pass a custom ID.
value
string|number|date
isContentMasked
boolean
- true (default)
false to make the input content visible by default or bind it to a variable to control the masking from outside the component.
isMultiline
boolean
- false (default)
<input>. If set to true it renders a <textarea>.
isInvalid
boolean
- false (default)
isRequired
boolean
- false (default)
Required indicator next to the label text and sets the required attribute on the control when user input is required.
isOptional
boolean
- false (default)
Optional indicator next to the label text when user input is optional.
visibilityToggleAriaLabel
string
- Show masked content (default)
aria-label for the visibility toggle button.
visibilityToggleAriaMessageText
string
- Input content is hidden (default)
aria-live message when the visibility toggle button is pressed.
hasCopyButton
boolean
- false (default)
true, it renders a Copy::Button next to the form control allowing the value of the input to be copied to the clipboard.
copyButtonText
string
- Copy masked content (default)
aria-label for the Copy::Button component.
width
string
@width parameter is provided, the control will have a fixed width. This width will only be applied to the control, not the other elements of the field.
height
string
@isMultiline is true. By default, the <textarea> has a height determined by the browser to accommodate 4 lines of text. If a custom @height value is provided, the control will have a fixed height.
extraAriaDescribedBy
string
aria-describedby HTML attribute.
By default, the
aria-describedby attribute is automatically generated by the component, using the IDs of the helper text and errors (if present). Use this argument to pass an extra ID.
…attributes
...attributes.
The attributes will be applied to the input control element. This means you can use all the standard HTML attributes of the input control element and all the usual Ember techniques for event handling, validation, etc.
Examples of HTML attributes:
name, placeholder, disabled, readonly, required. See the whole list of HTML attributes. Examples of Ember modifiers: {{on "input" [do something]}}, {{on "change" [do something]}}, {{on "blur" [do something]}}.
Contextual components
Label, HelperText, CharacterCount, and Error content are passed to the field as yielded components.
<[F].Label>
yielded component
<label> element. The content can be a simple string or a more complex/structured string, in which case it inherits the text style. For details about its API, check the Form::Label component.
The
for attribute of the label is automatically generated using the controlId value of the control.
<[F].HelperText>
yielded component
Form::HelperText component.
The
id attribute of the element is automatically generated using the controlId value of the control.
<[F].CharacterCount>
yielded component
Form::CharacterCount component.
The
id attribute of the element is automatically generated using the controlId value of the control.
<[F].Error>
yielded component
Form::Error component.
The
id attribute of the Error element is automatically generated.
<[E].Message>
yielded component
Error.Message.
Anatomy
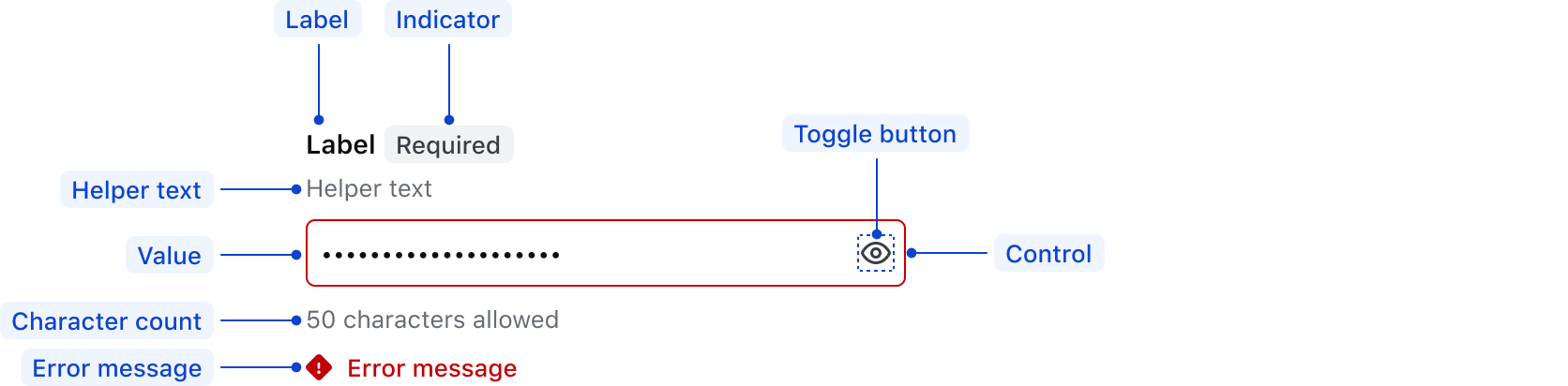
| Element | Usage |
|---|---|
| Label | Required |
| Indicator | Optional |
| Helper text | Optional |
| Placeholder/Value | Optional |
| Toggle button | Required |
| Control | Required |
| Error message | Triggered by system |
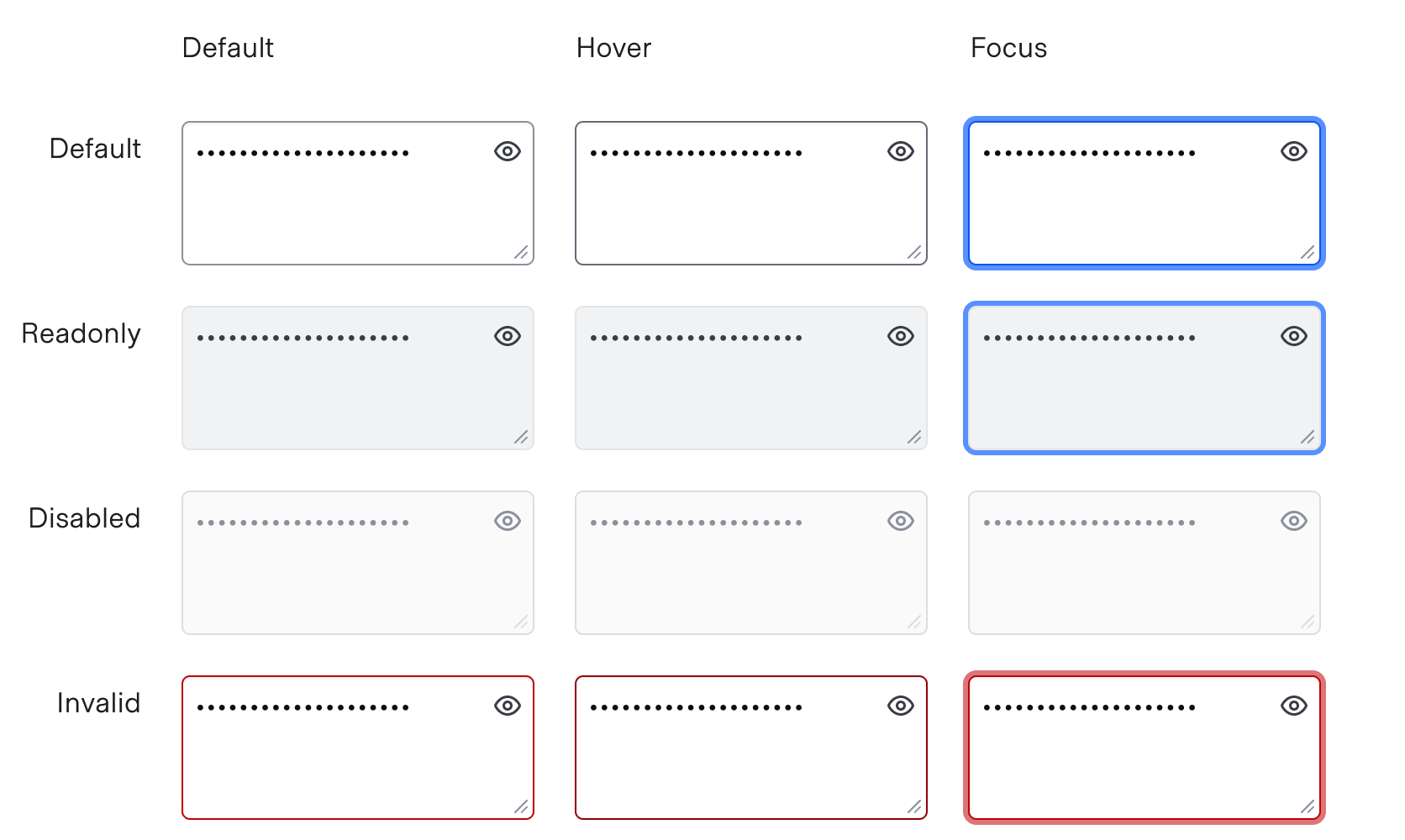
States
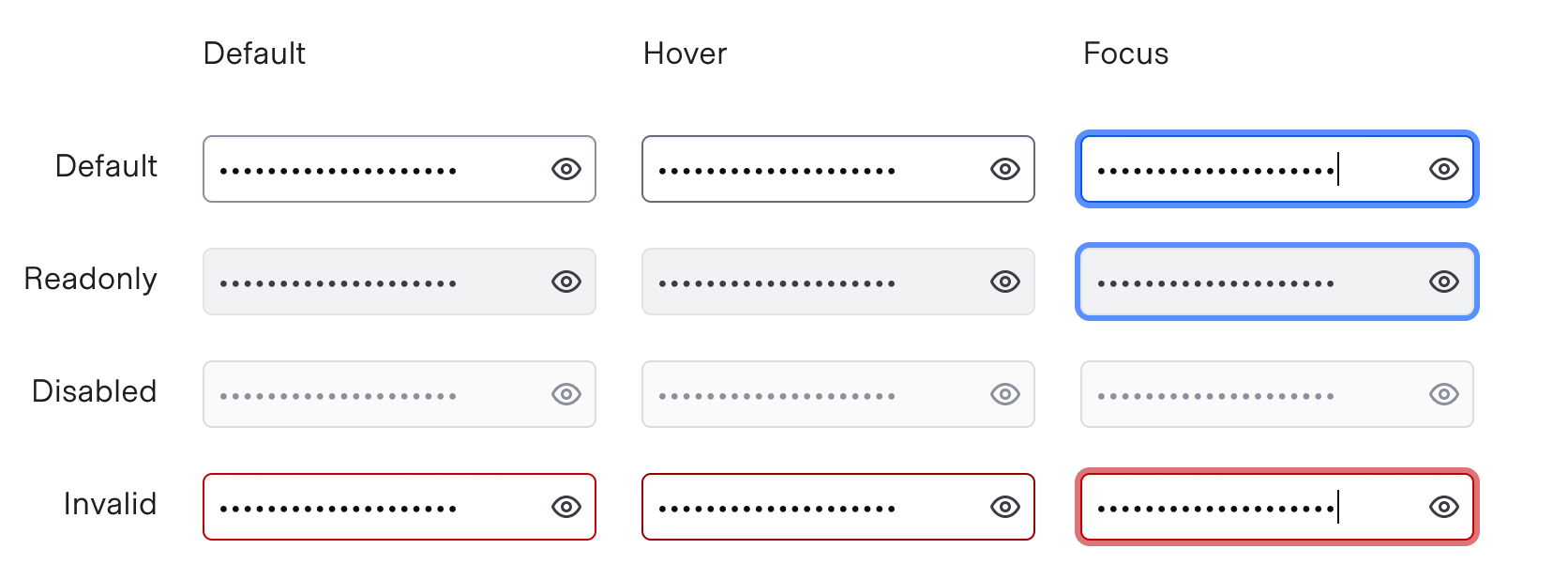
isMultiline
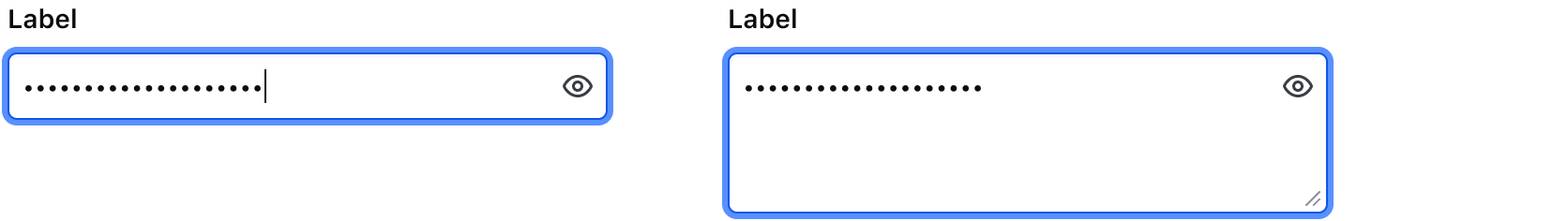
Keyboard navigation
Focus on the input
Move focus to the toggle button
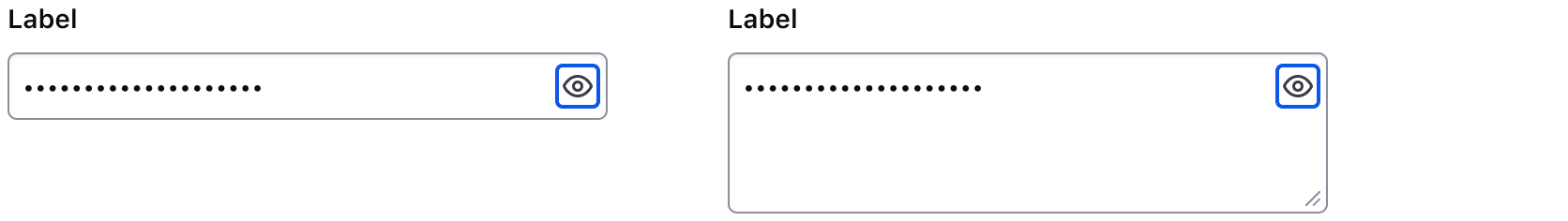
Activates toggle to show/hide the input value
Conformance rating
Form::MaskedInput::Field
Form::MaskedInput::Field is conformant when used as directed. For this reason, we recommend using Form::MaskedInput::Field when possible.
Form::MaskedInput::Base
Form::MaskedInput::Base is not conformant until it has an accessible name.
Known issues
If a link is used within a label, helper text, or error text, it will not be presented as a link to the user with a screen reader; only the text content is read out. As such, care should be used when considering this feature.
Applicable WCAG Success Criteria
This section is for reference only, some descriptions have been truncated for brevity. This component intends to conform to the following WCAG Success Criteria:
-
1.3.1
Info and Relationships (Level A):
Information, structure, and relationships conveyed through presentation can be programmatically determined or are available in text. -
1.3.2
Meaningful Sequence (Level A):
When the sequence in which content is presented affects its meaning, a correct reading sequence can be programmatically determined. -
1.3.4
Orientation (Level AA):
Content does not restrict its view and operation to a single display orientation, such as portrait or landscape. -
1.3.5
Identify Input Purpose (Level AA):
The purpose of each input field collecting information about the user can be programmatically determined when the input field serves a purpose identified in the Input Purposes for User Interface Components section; and the content is implemented using technologies with support for identifying the expected meaning for form input data. -
1.4.1
Use of Color (Level A):
Color is not used as the only visual means of conveying information, indicating an action, prompting a response, or distinguishing a visual element. -
1.4.10
Reflow (Level AA):
Content can be presented without loss of information or functionality, and without requiring scrolling in two dimensions. -
1.4.11
Non-text Contrast (Level AA):
The visual presentation of the following have a contrast ratio of at least 3:1 against adjacent color(s): user interface components; graphical objects. -
1.4.12
Text Spacing (Level AA):
No loss of content or functionality occurs by setting all of the following and by changing no other style property: line height set to 1.5; spacing following paragraphs set to at least 2x the font size; letter-spacing set at least 0.12x of the font size, word spacing set to at least 0.16 times the font size. -
1.4.3
Minimum Contrast (Level AA):
The visual presentation of text and images of text has a contrast ratio of at least 4.5:1 -
1.4.4
Resize Text (Level AA):
Except for captions and images of text, text can be resized without assistive technology up to 200 percent without loss of content or functionality. -
2.4.6
Headings and Labels (Level AA):
Headings and labels describe topic or purpose. -
2.4.7
Focus Visible (Level AA):
Any keyboard operable user interface has a mode of operation where the keyboard focus indicator is visible. -
3.2.1
On Focus (Level A):
When any user interface component receives focus, it does not initiate a change of context. -
3.2.2
On Input (Level A):
Changing the setting of any user interface component does not automatically cause a change of context unless the user has been advised of the behavior before using the component. -
3.2.4
Consistent Identification (Level AA):
Components that have the same functionality within a set of Web pages are identified consistently. -
3.3.1
Error Identification (Level A):
If an input error is automatically detected, the item that is in error is identified and the error is described to the user in text. -
3.3.2
Labels or Instructions (Level A):
Labels or instructions are provided when content requires user input. -
4.1.2
Name, Role, Value (Level A):
For all user interface components, the name and role can be programmatically determined; states, properties, and values that can be set by the user can be programmatically set; and notification of changes to these items is available to user agents, including assistive technologies.
Support
If any accessibility issues have been found within this component, let us know by submitting an issue.
4.12.0
Changed textarea scrollbar-width to thin to reduce overlap with toggle button.

